Evaporative Condenser
An evaporative condenser is a type of heat exchanger commonly used in refrigeration and air conditioning systems. It combines the functions of a condenser and a cooling tower by using water evaporation to remove heat from the refrigerant. Here’s a brief description of its operation:
Heat Exchange
Hot refrigerant vapor from the compressor enters the evaporative condenser coil.
Water Spray
Water is continuously sprayed over the condenser coil. As the water flows over the coil, it evaporates and absorbs heat from the refrigerant inside the coil.
Heat Removal
The heat from the refrigerant is transferred to the water through evaporation. This lowers the temperature of the refrigerant vapor, causing it to condense into liquid form.
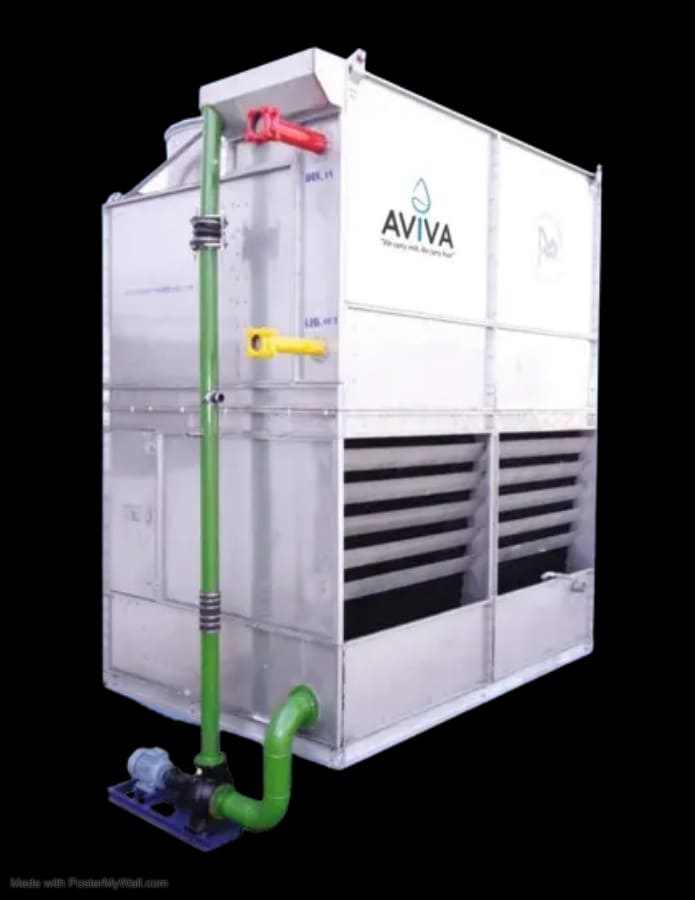
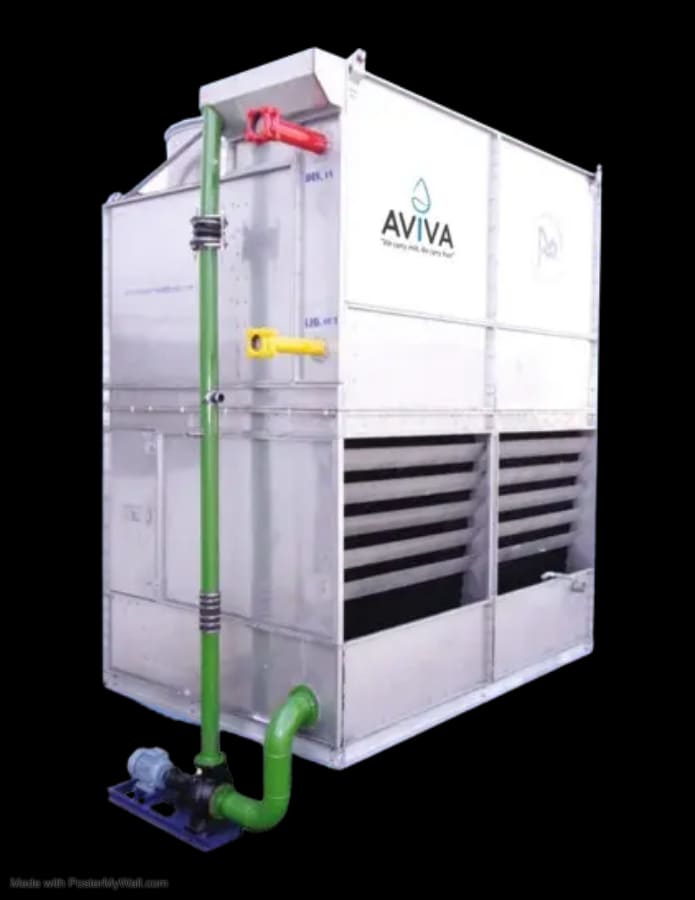


Cooling Tower Effect
The warm water, now heated from absorbing the refrigerant’s heat, is collected at the bottom of the condenser and either recycled back into the system or disposed of. This process is akin to a cooling tower where heat is dissipated through evaporation.
Efficiency
Evaporative condensers are efficient because they utilize both air and water to cool the refrigerant, making them suitable for large-scale cooling applications where water conservation is feasible.
Overall, evaporative condensers are valued for their energy efficiency and ability to handle large heat loads effectively in industrial and commercial settings.